RFID
RFID - Radio Frequency Identification
Our company has been professionally dedicated to UHF RFID (Ultra-High Frequency Radio Frequency Identification) technology since its inception. This technology has become a key tool in the field of tracking and identification of objects over longer distances. UHF RFID enables accurate and efficient tracking of goods, inventory, and even people, in real time and over distances of several meters.
We have a team of certified system engineers whose experience guarantees reliably implemented RFID projects. From manufacturing operations, through logistics, warehousing and business processes to asset registration, RFID technology can be applied everywhere and we can implement complex projects there.
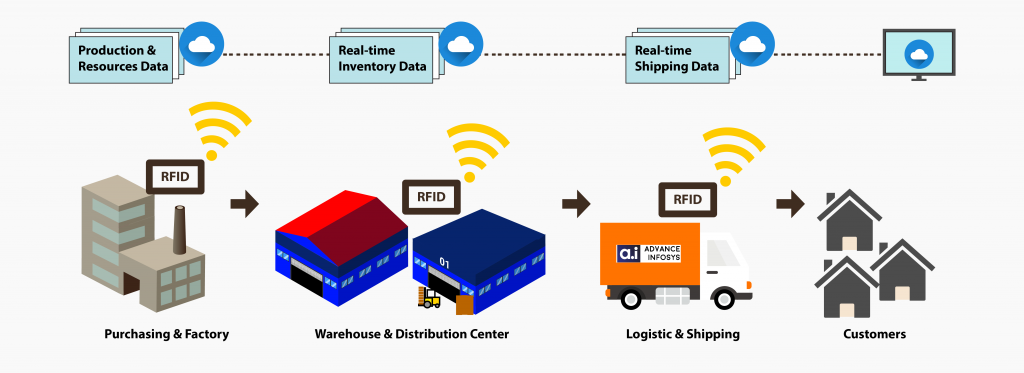
RFID systems are modern contactless automatic identification systems that provide a perfect overview of all operations in real time
What is UHF RFID?
UHF RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a wireless data transmission technology that operates in the frequency range from 860 MHz to 960 MHz. This frequency range allows UHF RFID tags to communicate with readers over longer distances. This makes the technology suitable for applications where a large number of objects need to be quickly identified over longer distances, without the need for direct contact or visual visibility between the reader and the tag.
How does UHF RFID work?
UHF RFID technology works on the principle of transmitting and receiving electromagnetic waves between the RFID tag and the RFID reader. This process takes place in several steps:
1. Transmission of the signal by the reader: The RFID reader generates electromagnetic waves in the UHF frequency range (860-960 MHz). These radio waves propagate into the surroundings and can activate RFID tags that are within range.
2. Tag activation: when a passive UHF RFID tag comes within range of the reader, its antenna picks up the electromagnetic waves and uses this energy to activate the microchip. Active tags, which have their own power source, are able to transmit data over longer distances without the need for external power.
3. After activation, the tag sends its unique identification number (EPC) back to the RFID reader. This communication is very fast, allowing the reader to identify many tags at once.
4. Data processing.
UHF RFID tags and EPC
UHF RFID tags are small devices equipped with a microchip and an antenna. Tags can be passive or active:
- Passive UHF RFID tags: They do not have their own power source. They use the energy they capture from the electromagnetic waves emitted by the reader. They have a shorter range but are cheaper and suitable for mass production.
- Active UHF RFID tags: contain a battery that allows them to transmit signals over longer distances. Active tags are more expensive, but their ability to transmit signals in more challenging environments (e.g., through metals or liquids) makes them a valuable tool for specific applications.
Each RFID tag is equipped with a unique identification code, known as an EPC (Electronic Product Code). EPC is the international standard for product identification and enables unique identification of individual items within the global supply chain. This code contains information about the manufacturer, the product and, where applicable, the serial number, making it a key element for tracking goods at a global level.
As a carrier of information,the RFID tag can be in the form of a label (Smart label) or in an encapsulated form of various shapes, sizes and materials. To read and write data to RFID tags, an RFID reader in a stationary or mobile version is used.
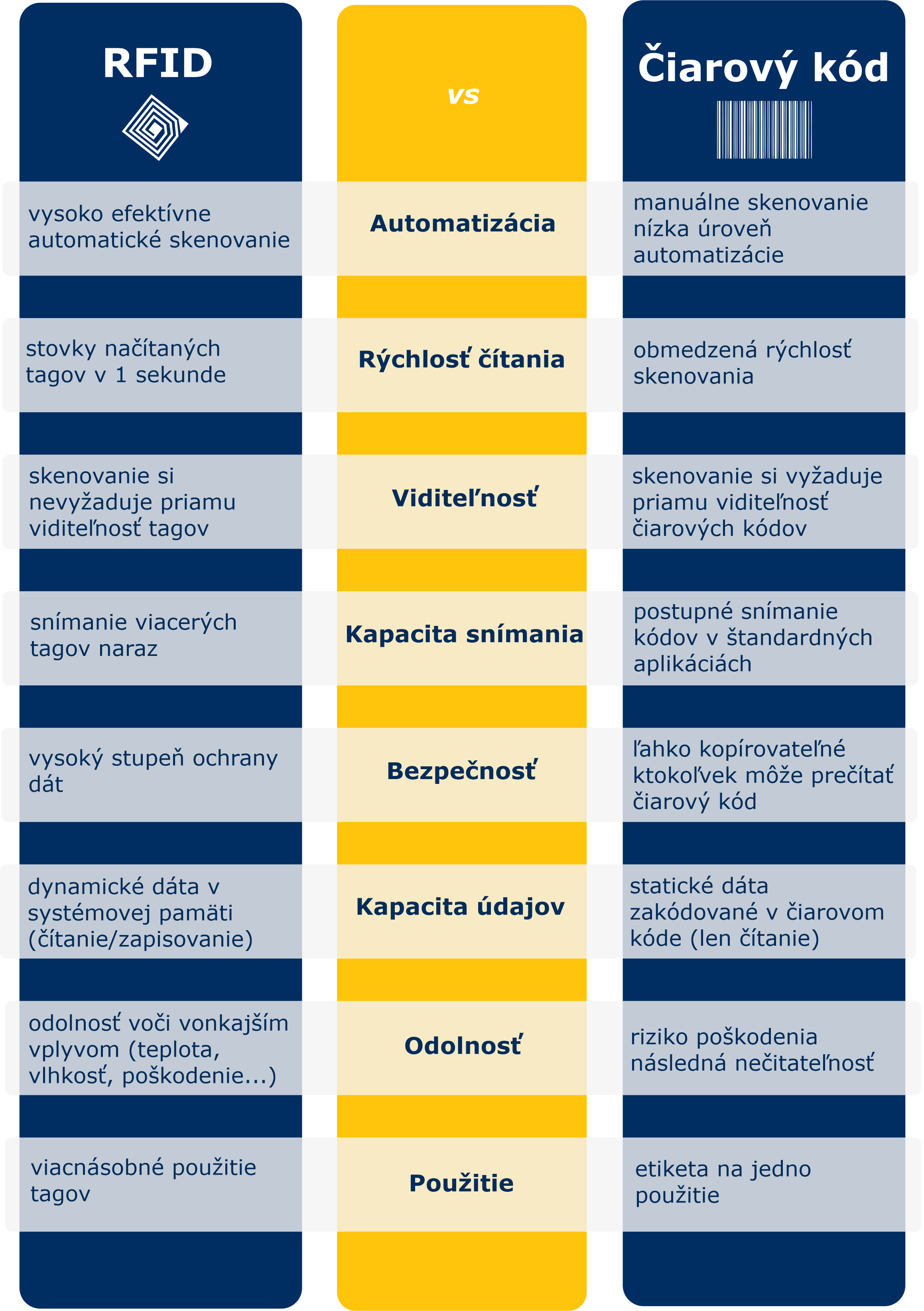
Why RFID?
Although barcode identification technology is the most widespread and accessible, it may not be sufficient in some cases. The barcode can be replaced by a tag (label), which is a chip connected to an antenna that allows information to be written and read wirelessly.
RFID as a replacement for barcodes?
RFID technology is not intended to replace barcodes, but rather to complement them. In a wide range of applications, a combination of the two technologies is most advantageous.
Economic benefits of RFID
⇒ More products for the same fixed cost
⇒ greater accuracy in picking, easier inventory
⇒ minimisation of labelling and relabelling costs
⇒ faster picking, receiving, sorting and selection
⇒ improved asset recording and handling
⇒ simplification in data management and exchange
⇒ fast return on investment
The future of UHF RFID technology
With the development of technology and the growing importance of automation and the Internet of Things (IoT), UHF RFID has a promising future ahead of it. Some of the expected trends include:
1. Integration with IoT: In conjunction with IoT, UHF RFID tags are expected to serve as the essential link between physical objects and the digital world. They will enable devices and objects to "talk" to each other, opening up new possibilities for smart cities, warehouses and homes.
2. Advanced sensors in RFID tags: RFID tags are expected to be integrated with sensors that can monitor factors such as temperature, humidity or pressure. These tags could be used in healthcare, food and pharmaceutical applications to monitor product storage conditions and ensure product quality.
3. Expansion into new industries: In the future, RFID technology is expected to be widely used in industries where it has not yet been implemented en masse, such as agriculture, aerospace, and construction.
4. With the increasing number of UHF RFID systems, it will be important to address security and data protection issues. The development of encryption technologies and security protocols are expected to protect data transmitted between tags and readers.
How can KODYS Slovakia help in the implementation of RFID technology in enterprises?
- Consulting and advisory services.
- Supply and integration of hardware and middleware.
- Service and support.




